In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, cloud computing has become a cornerstone for data analytics. This transformation enables businesses to leverage vast amounts of data for informed decision-making, agile operations, and innovative solutions. However, with the increasing reliance on cloud environments, data security concerns have become paramount. This article delves into the importance of data security in cloud computing, specifically for data analysts, and offers insights and best practices to maintain robust security protocols.
Mục lục
- 1 Overview of Data Security in Cloud Computing for Data Analysts
- 2 Best Practices for Data Security in Cloud Computing
- 3 The Shared Responsibility Model in Cloud Security
- 4 Importance of Encryption and Access Control for Data Analysts
- 5 Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response
- 6 Compliance and Regulatory Issues in Cloud Security
- 7 Best Practices for Ensuring Data Security in the Cloud
- 8 Future Trends in Cloud Security Relevant to Data Analysts
- 9 Conclusion
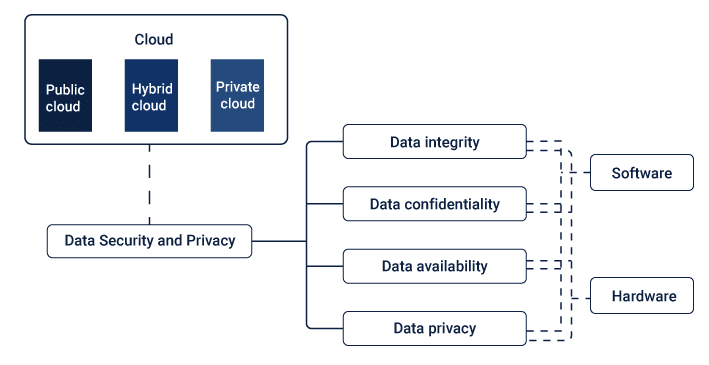
Overview of Data Security in Cloud Computing for Data Analysts

As a data analyst, your role is pivotal in extracting meaningful insights from the abundance of data available on cloud platforms. However, along with this responsibility comes the crucial task of safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining data integrity. In this section, we will discuss the key elements of data security that are essential for any data analyst working with cloud-based systems.
Authentication and Authorization
One of the primary concerns in cloud computing is ensuring secure access to resources. As a data analyst, you will likely have privileged access to critical datasets stored on cloud platforms. It is vital to implement robust authentication methods such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strong passwords to prevent unauthorized access. Additionally, setting up strict authorization policies can limit access only to necessary resources, minimizing the risk of data breaches.
Data Encryption
Data encryption is a critical aspect of data security in cloud computing. It involves converting plain text into code to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. As a data analyst, you may be dealing with personally identifiable information (PII), financial records, or other sensitive data that must be encrypted before being stored on the cloud. Some best practices for data encryption include using strong encryption algorithms and regularly rotating encryption keys.
Regular Backups
In an increasingly digital landscape, data loss can have severe consequences for businesses. That’s why it is crucial to regularly back up your data on the cloud to prevent any catastrophic events such as hardware failures or cyber attacks. As a data analyst, you should also consider implementing disaster recovery plans and conducting routine data audits to ensure the integrity of your backups.
Best Practices for Data Security in Cloud Computing

Apart from the essential elements, here are some best practices that can help you enhance the security of your data on cloud platforms:
- Conduct regular security assessments: It is vital to conduct regular vulnerability scans and penetration tests to identify any potential security gaps and address them promptly.
- Educate users on data security: As a data analyst, you must educate your team members on proper data handling procedures, including secure file sharing, password management, and recognizing suspicious activities.
- Implement role-based access controls: Role-based access controls allow you to define user permissions based on their roles in the organization. This ensures that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data, reducing the risk of insider threats.
- Monitor and log activities: Monitoring and logging activities on cloud platforms can help you identify any suspicious behavior or attempted breaches. It is crucial to set up alerts for any unusual activity that may indicate a security breach.
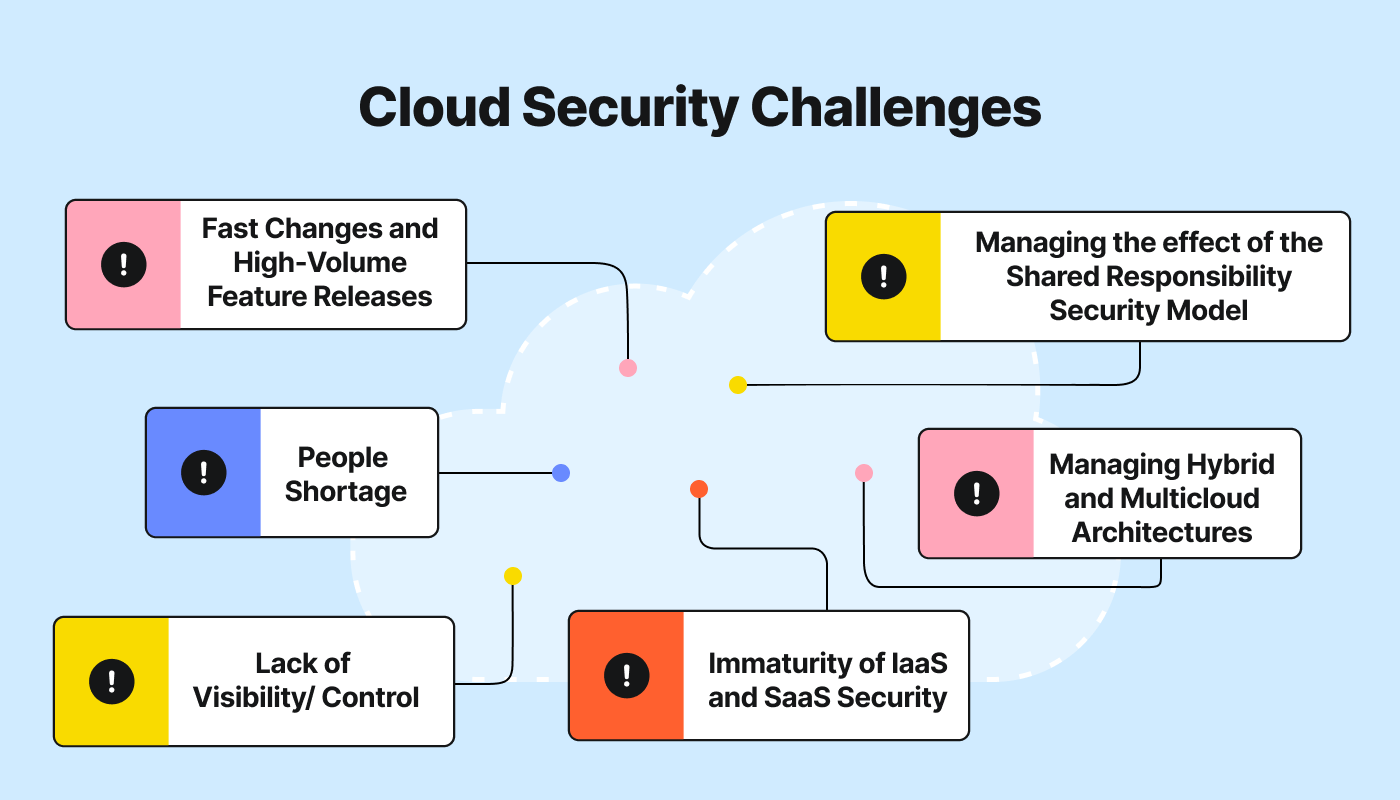
One important concept to understand in cloud security is the shared responsibility model. This model outlines the division of security responsibilities between cloud service providers (CSPs) and their customers. While CSPs are responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure, data analysts must ensure the security of their data and applications on the cloud. It is essential to understand this shared responsibility and take necessary precautions to protect your data.
The shared responsibility model delineates the division of security responsibilities between cloud service providers and users. While cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud ensure the security of the cloud infrastructure, data analysts and organizations are responsible for securing their data within the cloud. This includes data encryption, access control, and data backups.
As a data analyst working with cloud platforms, understanding the shared responsibility model is crucial. It helps you identify your role in securing your data and understand the measures that CSPs have in place to protect their infrastructure. By implementing best practices and adhering to security protocols outlined by the CSP, you can work towards maintaining robust data security on the cloud.
Importance of Encryption and Access Control for Data Analysts
Encryption and access control are two crucial aspects of data security that hold particular importance for data analysts. As mentioned earlier, encrypting sensitive information can prevent unauthorized access and ensure the confidentiality of your data. Similarly, implementing strict access controls ensures that only authorized personnel have the necessary permissions to view or manipulate critical datasets.
Role of Encryption
Encryption functions as the first line of defense against unauthorized data access. As a data analyst, you often work with sensitive information, including customer data and financial records, making it imperative to implement strong encryption methods. The role of encryption extends beyond just data at rest; it is also crucial for data in transit. Utilize Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols to secure data being transmitted between systems, ensuring that intercepted data cannot be read or altered. Additionally, familiarize yourself with encryption standards such as AES-256, which is widely recognized for its robustness in protecting sensitive data.
Role of Access Control
Access control plays a pivotal role in safeguarding data by restricting access to authorized users only. Implementing role-based access controls (RBAC) is a fundamental strategy for data analysts to ensure that sensitive information is only accessible to individuals with the appropriate permissions. By defining user roles and assigning access rights based on job functions, you can mitigate the risk of unauthorized data exposure and potential security breaches. Moreover, adopting the principle of least privilege (PoLP) – whereby users are granted the minimum level of access necessary to perform their tasks – can further enhance the security posture of your cloud environment. Regularly reviewing and auditing access controls ensures compliance with security policies and helps to identify any potential vulnerabilities that need addressing.
Implementing Access Control
Access control serves as a barrier against unauthorized access to critical data. Implementing role-based access control (RBAC) is an effective way to manage permissions based on user roles within your organization. This ensures that employees can only access the data necessary for their job functions, thereby minimizing the risk of data breaches. Additionally, consider using attribute-based access control (ABAC) where access rights are granted through the use of policies that combine various attributes such as user role, geographic location, and the time of access. Regularly review and update access controls to accommodate changes in team roles or organizational structure.
Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response
Continuously monitoring your cloud environment is essential to detect and respond to potential security threats in real time. Set up automated monitoring tools to track unusual activities and generate alerts for any suspicious behavior. Implementing a robust incident response plan is crucial to minimize the impact of security breaches. This involves identifying the immediate steps to contain the breach, analyzing the incident to understand its root cause, and taking corrective actions to prevent future occurrences.
Utilizing Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems
SIEM systems are invaluable tools in the realm of continuous monitoring. They aggregate and analyze activity from multiple resources across your IT infrastructure, helping to identify security threats that may not be apparent when looking at individual events. As a data analyst, leveraging SIEM systems enables you to detect patterns indicative of a potential breach, thus allowing for timely intervention.
Incident Response Planning
Proactive incident response planning is essential to ensure that your team can act swiftly and effectively in the event of a security breach. Develop and document clear procedures for identifying, reporting, and mitigating security incidents. Conduct regular drills and simulations to ensure that all team members are familiar with their roles and responsibilities during an actual incident. The goal is to minimize damage, preserve evidence for forensic analysis, and restore normal operations as quickly as possible.
Compliance and Regulatory Issues in Cloud Security

Cloud security compliance and regulatory requirements are ever-evolving, making it crucial for data analysts to stay informed about the latest developments. Depending on the industry you work in or the type of data you handle, various regulations may apply to your organization. Some examples include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). It is essential to understand these regulations and ensure that your cloud environment is compliant through regular risk assessments and audits.
Major Compliance Standards for Data Analysts
The GDPR is a comprehensive data privacy regulation that applies to all organizations handling personal data of individuals within the European Union (EU). It requires strict adherence to data protection principles, including consent, transparency, and accountability. HIPAA regulates the use and disclosure of protected health information in the healthcare industry, with specific requirements for security measures to protect this sensitive information. PCI DSS applies to organizations that handle credit card payments and requires robust security controls to safeguard cardholder data.
Risk Assessments and Audits
Regular risk assessments and audits are crucial in maintaining compliance with various regulations. These assessments help identify potential vulnerabilities and areas where security controls may be lacking. By conducting regular internal audits or hiring external auditors, you can ensure that your organization remains compliant and identify any areas for improvement. It is also essential to keep track of any changes in compliance requirements and adjust your security measures accordingly.
Several compliance standards are pertinent to cloud security:
- HIPAA: Governs the protection of health information.
- GDPR: Regulates data protection and privacy in the European Union.
- SOC 2: Focuses on managing customer data based on five “trust service principles”—security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
Challenges and Best Practices for Compliance
One of the main challenges in maintaining compliance in the cloud is the dynamic nature of cloud environments. As organizations scale and evolve, they often adopt new services, technologies, and configurations that can introduce unforeseen compliance issues. To address these challenges, it is crucial to implement continuous compliance monitoring. This involves using automated tools to track changes in the cloud infrastructure and ensure they do not violate compliance requirements. Additionally, organizations should stay updated on changes in relevant regulations and adjust their policies and procedures accordingly.
Best Practices for Ensuring Data Security in the Cloud
As a data analyst, you play an essential role in ensuring the security of your organization’s data in the cloud. Here are some best practices to keep in mind:
- Implement multi-factor authentication for all users accessing sensitive data or systems.
- Regularly back up your data and test the backups to ensure they can be restored if needed.
- Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit, using industry-standard encryption algorithms.
- Use secure coding practices when developing applications that handle sensitive data.
- Regularly review access controls and permissions to ensure they align with business needs and compliance requirements.
- Train employees on cybersecurity best practices, such as identifying phishing emails and reporting suspicious activities.
By following these best practices, you can help protect your organization’s data from potential security threats in the cloud. It is also crucial to stay informed about emerging security trends and continuously assess and update your security measures to address any potential vulnerabilities. With a proactive approach, you can mitigate the risks of data breaches and ensure the safety and confidentiality of your organization’s valuable information.
Future Trends in Cloud Security Relevant to Data Analysts
As cloud technology continues to evolve, several emerging trends are shaping the landscape of cloud security. These trends are particularly relevant to data analysts, who must stay abreast of the latest developments to effectively protect their organization’s data.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are becoming increasingly integral in enhancing cloud security. These technologies enable the analysis of vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate security threats. For data analysts, leveraging AI and ML can streamline the detection of vulnerabilities and the response to potential breaches. By automating routine tasks, AI and ML can also free up analysts to focus on more strategic security efforts.
Zero Trust Security Model
The zero trust security model is gaining traction as organizations seek more robust ways to secure their cloud environments. This model operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” requiring continuous authentication and authorization of all users and devices, both inside and outside the network perimeter. Implementing a zero trust architecture involves closely monitoring user activities, segmenting networks, and enforcing strict access controls. Data analysts play a crucial role in analyzing the data and insights generated from zero trust systems to ensure compliance and security.
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) combines network security services with wide area network (WAN) capabilities to deliver a holistic approach to cloud security. SASE solutions integrate multiple security functions, such as secure web gateways, firewalls, and zero trust network access, into a single cloud-delivered service. This approach simplifies security management and enhances protection for cloud environments. Data analysts can benefit from SASE by gaining centralized visibility and control over network security, helping to identify and mitigate potential threats more efficiently.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing holds the potential to significantly impact cloud security, both positively and negatively. On one hand, quantum computers could break current encryption algorithms, posing a substantial threat to data security. On the other hand, advancements in quantum-resistant encryption algorithms are being developed to counteract these risks. Data analysts must stay informed about the progress in quantum computing and its implications for cloud security to proactively address emerging challenges.
Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs)
Privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) are becoming more critical as data privacy concerns continue to rise. PETs include techniques such as homomorphic encryption, differential privacy, and secure multi-party computation, which allow data to be processed and analyzed without exposing it to unauthorized parties. For data analysts, adopting PETs can enable the secure analysis of sensitive data while maintaining compliance with privacy regulations.
By understanding and adapting to these future trends, data analysts can play a pivotal role in safeguarding their organization’s data and maintaining robust cloud security. Continuous learning and staying updated on technological advancements are essential to addressing emerging threats and ensuring the effective protection of valuable data assets.
Conclusion
In conclusion, data security in cloud computing is a critical concern for data analysts. By understanding the shared responsibility model, implementing robust encryption and access control measures, adhering to compliance standards, and following best practices, data analysts can effectively safeguard their data. As Gartner Research highlights, “Security and risk management leaders must remain vigilant and proactive to navigate the evolving threat landscape.”
Stay informed, stay secure, and take the necessary steps to protect your data in the cloud today. For more in-depth insights and tools, consider signing up for Jasper for free to explore the full potential of AI in data security.