In today’s digital age, protecting Personally Identifiable Information (PII) is more critical than ever. As data privacy enthusiasts, understanding the significance of PII and the measures required to safeguard it can help us mitigate risks and foster a culture of security. This article will delve into the essentials of PII protection, providing insights into best practices, regulatory compliance, and emerging trends.
Mục lục
What Constitutes PII?

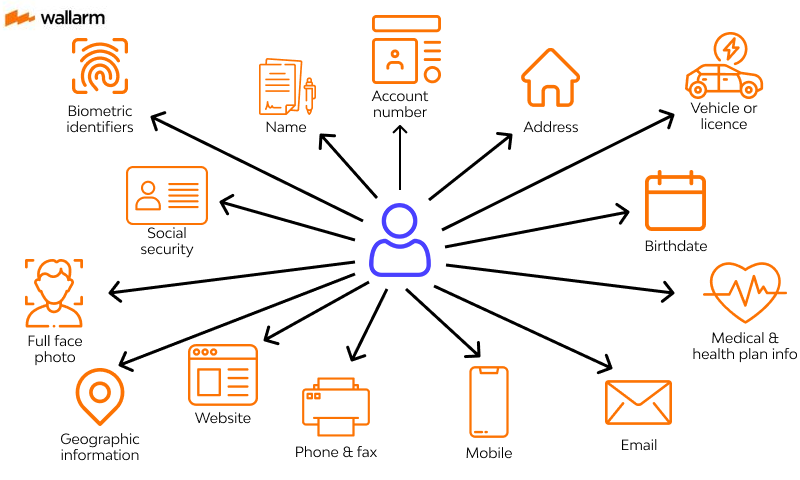
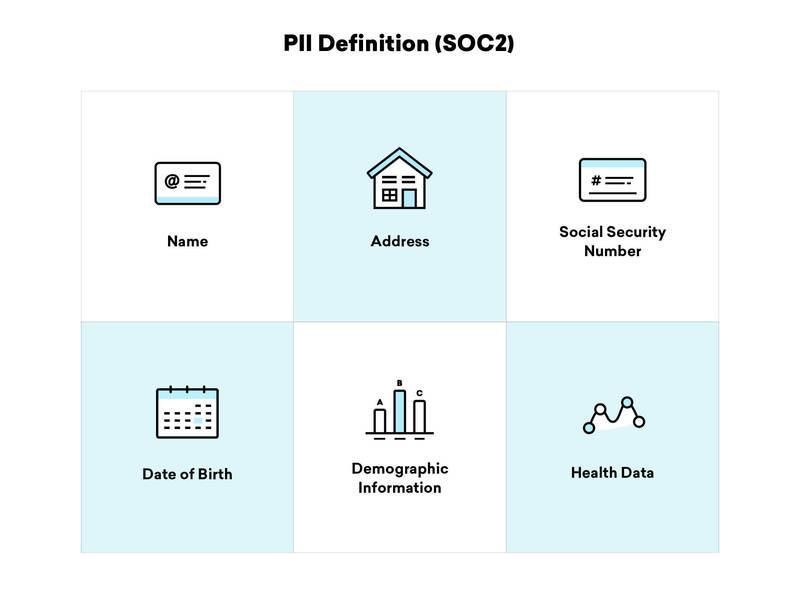
PII, also known as sensitive personal information or personal data, is any information that can be used to identify an individual uniquely. This includes both direct and indirect identifiers such as names, email addresses, phone numbers, social security numbers, driver’s license numbers, credit card details, biometric data, and more. With the increasing amount of data being collected and shared online, it has become crucial to identify and protect PII from unauthorized access or misuse.
Why is PII Protection Important?
PII protection is vital for both individuals and organizations. For individuals, the exposure of their sensitive personal information can lead to identity theft and financial fraud. On the other hand, organizations that fail to protect PII face not only legal consequences but also damage
PII refers to any information that can be used to identify an individual, either directly or indirectly. Common examples include:
- Personal Identifiers: Name, social security number, driver’s license number, passport number, etc.
- Contact Information: Address, email address, phone number, etc.
- Financial Information: Bank account details, credit card information, income records, etc.
- Health and Medical Records: Medical history, insurance information, prescription details, etc.
- Biometric Data: Fingerprints, retina scans, voice patterns, DNA profiles.
Sensitive vs. Non-Sensitive PII
Sensitive PII includes information that, when disclosed, could result in significant harm to the individual, such as financial loss or identity theft. Examples of sensitive PII are social security numbers, passport numbers, and biometric data. Non-sensitive PII, on the other hand, is information that, when by itself, is not likely to cause harm, such as a person’s zip code or date of birth. However, when combined with other data, non-sensitive PII can still pose a risk.
Risks and Consequences of PII Misuse

The misuse of PII can have severe consequences for individuals and organizations. Some of the risks associated with unauthorized access or disclosure of PII include:
Identity Theft and Fraud
Identity theft and fraud are perhaps the most well-known risks associated with the misuse of PII. When malicious actors gain access to sensitive personal information, they can impersonate individuals to commit various forms of fraud. This includes opening credit accounts, securing loans, or even filing false tax returns in the victim’s name. The repercussions can be long-lasting, affecting a person’s credit score and financial stability.
Legal and Regulatory Consequences
Organizations that fail to protect PII face significant legal and regulatory repercussions. Various regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, mandate stringent measures for the protection of personal data. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and legal actions, alongside damage to the organization’s reputation. This underscores the necessity for businesses to implement robust PII protection protocols and ensure adherence to international and local regulations.
Damage to Reputation
Beyond legal and financial consequences, the mishandling of PII can severely damage an organization’s reputation. Trust is paramount in any customer relationship, and a data breach can erode that trust irrevocably. Companies found negligent in protecting PII often face backlash from the public and lose customer loyalty. Rebuilding a tarnished reputation requires significant effort, time, and resources, which underscores the importance of proactive and comprehensive PII protection strategies.
Best Practices for Protecting PII
To mitigate the risks associated with PII misuse, organizations should adopt a multifaceted approach to data protection. Here are some best practices to consider:
Data Encryption
Encrypting PII both at rest and in transit ensures that unauthorized parties cannot access the data without the proper decryption keys. This adds a critical layer of security, particularly when data is transferred over the internet or stored in cloud environments.
Access Controls
Implementing stringent access controls is essential to limit who can view or manipulate PII. This can be achieved by using role-based access control (RBAC), where access rights are assigned based on the user’s role within the organization. Regular audits of access logs can further enhance security by identifying and addressing unauthorized access attempts.
Regular Audits and Assessments
Periodic security audits and risk assessments help identify vulnerabilities within an organization’s data protection framework. These assessments should be conducted regularly to ensure that security measures are up-to-date and effective in mitigating new and evolving threats.
Employee Training and Awareness
Human error is often a significant factor in data breaches. Comprehensive training programs can educate employees on the importance of PII protection and the best practices for maintaining data security. Regularly updating these training programs ensures that employees are aware of the latest threats and how to counteract them.
Incident Response Plan
Having a well-defined incident response plan in place is crucial for promptly addressing data breaches. This plan should outline the steps to take when a breach is detected, including notification procedures, containment strategies, and remediation efforts. An effective incident response plan can significantly reduce the impact of a data breach on both the organization and the impacted individuals.
By implementing these best practices, organizations can enhance their PII protection efforts and safeguard sensitive personal information from misuse and unauthorized access.
Compliance with Data Protection Regulations
As mentioned earlier, various regulations have been put in place to protect individuals’ personal data. These regulations not only mandate the protection of PII but also provide individuals with certain rights regarding their personal information. Some common rights under data protection regulations include:
- Right to Access: Individuals have the right to request access to their personal data and how it is being used.
- Right to Rectification: If an individual’s PII is incorrect or incomplete, they can request for it to be corrected.
- Right to Erasure: Also known as the “right to be forgotten,” this allows individuals to request the deletion of their personal data.
- Right to Data Portability: Individuals can ask for a copy of their PII in a commonly used format.
- Right to Object: Individuals can object to the processing of their personal data for specific purposes, such as direct marketing.
Organizations must comply with these regulations and provide individuals with these rights when handling their PII. Failure to do so can result in legal and financial consequences, as discussed earlier.
Overview of GDPR, CCPA, and Other Relevant Laws
Data protection regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) set stringent guidelines for handling PII. Organizations must adhere to these laws to avoid penalties and ensure the privacy of their users.
The Impact of Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with data protection regulations can lead to severe consequences, including substantial fines, legal actions, and loss of customer trust. For instance, GDPR non-compliance can result in fines amounting to 4% of a company’s global annual revenue. Similarly, the CCPA allows for fines of up to $7,500 per violation. These numbers highlight the importance of compliance with data protection laws and the potential consequences of non-compliance.
The Role of Individuals and Organizations in PII Protection

Protecting PII is a shared responsibility between individuals and organizations. Individuals must be cautious about sharing their personal information, especially online, to reduce the risk of identity theft and other forms of cybercrime. Organizations, on the other hand, have a legal and ethical obligation to protect the PII they collect from their customers or employees.
Both parties can take proactive steps to enhance PII protection. For example, individuals can use unique passwords for different accounts and enable two-factor authentication when possible. Organizations should prioritize data security by implementing robust encryption measures, access controls, regular audits, and employee training programs.
Importance of Awareness and Education
One of the most crucial aspects of PII protection is awareness and education. Individuals must understand the potential risks associated with sharing their personal information and learn how to protect themselves from these threats. Organizations should also prioritize educating their employees about data privacy and security best practices to minimize human error in handling PII.
Responsibility for Safeguarding PII in the Modern Age
As technology continues to advance, the responsibility of safeguarding PII becomes more critical. Organizations must keep up with evolving threats and implement robust security measures to protect sensitive personal information. Similarly, individuals must also stay informed about data privacy and take necessary precautions to protect their PII.
Emerging Trends and Technologies in PII Protection

The landscape of PII protection is constantly evolving, and new technologies are being developed to enhance data security. Some of the emerging trends and technologies in PII protection include:
- Blockchain: This technology offers a decentralized approach to storing and sharing data, making it more secure against potential breaches.
- Zero-trust architecture: This security model assumes that no user or device can be trusted within a network, requiring strict authorization for all access requests.
- Data masking: This technique involves disguising sensitive data by replacing actual values with fictitious ones, reducing the risk of exposure in case of a breach.
As these technologies continue to develop, organizations must stay informed and consider implementing them as part of their overall PII protection strategy.
Biometric Data and Multi-Factor Authentication
Biometric data, such as fingerprint scans, facial recognition, and voice patterns, are becoming increasingly popular as a method of enhancing security. Unlike traditional passwords, biometric data is unique to each individual, making it much harder for unauthorized users to gain access. Incorporating biometric data into multi-factor authentication (MFA) processes can significantly bolster security by requiring multiple forms of verification before granting access.
Multi-factor authentication combines something the user knows (like a password), something the user has (like a smartphone), and something the user is (such as a fingerprint or facial recognition). This layered approach ensures that even if one factor is compromised, the others can still protect the account. MFA has been shown to reduce the risk of unauthorized access and is considered a best practice for safeguarding sensitive information.
Privacy Concerns and Ethical Considerations with Biometrics
While the use of biometric data in security is beneficial, it also raises significant privacy concerns and ethical considerations. Biometric data is deeply personal and, once compromised, cannot be changed like a password. Therefore, organizations must handle biometric data with the highest level of security and transparency. There are also concerns regarding consent and how biometric data is collected, stored, and used. It is crucial for organizations to obtain clear, informed consent from individuals before collecting their biometric data and to provide robust data protection measures to safeguard it.
The Future of PII Protection
Looking ahead, the protection of PII will continue to be a dynamic field, driven by technological advancements and evolving regulatory landscapes. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into cybersecurity solutions offers promising avenues for identifying and mitigating threats in real-time. Additionally, as global data protection regulations become more stringent, organizations will need to enhance their compliance efforts to avoid severe penalties and maintain customer trust. In this rapidly changing landscape, staying informed and proactive about PII protection is essential for both individuals and organizations. As technology continues to advance, the responsibility of safeguarding PII becomes more critical. Organizations must keep up with evolving threats and implement robust security measures to protect sensitive personal information. Similarly, individuals must also stay informed about data privacy and take necessary precautions to protect their PII.
Conclusion
Protecting PII is paramount in maintaining data privacy and preventing identity theft, fraud, and privacy violations. By understanding what constitutes PII, recognizing potential risks, and adopting best practices, individuals and organizations can effectively safeguard sensitive information.
As technology continues to evolve, new methods and tools for protecting PII will emerge. Staying informed about the latest trends and regulations is crucial for maintaining robust data privacy practices.